What are Geographical Constraints?
Geographical constraints refer to the physical conditions and limitations that impact route planning and optimization. The physical limitation can be in the form of a geographical area that includes terrain, traffic conditions, and infrastructure.
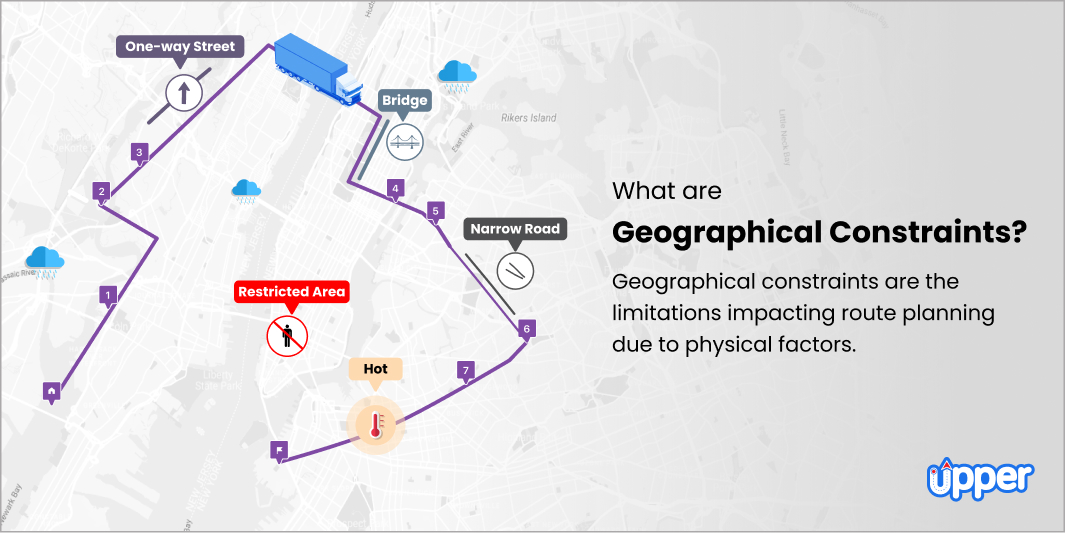
Businesses need to consider various geographical constraints to ensure efficient transportation while optimizing the routes. Furthermore, factors like narrow roads, bridges, or tunnels can also impose restrictions on vehicle size or weight that will affect the route selection or navigation.
Hence, it becomes important to effectively manage the geographical constraints to streamline logistics, reduce costs, enhance customer service, and also minimize the environmental impact.
Types of Geographical Constraints
Understanding the types of geographical constraints is crucial for effective planning and decision-making for any business. Some key types of geographical constraints are:
Road network restrictions
It includes restrictions, such as one-way streets, restricted areas, or road closures. However, handling these constraints requires careful consideration to avoid any erroneous detours and also ensure compliance at the same time.Traffic conditions
This geographical constraint considers congestion, peak hours, and traffic flow patterns. Therefore, it is a must to consider these dynamic factors while optimizing routes to avoid any delays and ensure deliveries on time.Terrain and topography
The geographical constraint terrain and topography take into account the steep slopes, narrow roads, and rough terrains. And these constraints would require route adjustments or considering alternative paths as they can affect vehicle safety as well as performance.Weather conditions
Weather fluctuations, such as rain, snow, or extreme temperatures, can significantly impact the condition of the roads and pose challenges to transportation. Therefore, route optimization must be considered to ensure efficient and safe travel.Access restrictions
The access restriction can be in the form of bridges, tunnels, or weight restrictions for certain vehicles. So, following these restrictions can avoid any type of legal issues and improve business operations.
This is how understanding various types of geographical constraints can help businesses to develop robust strategies leading to smooth logistics operations and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Implications of Geographical Constraints
Geographical constraints come up with several challenges that impact the transportation operation. Here are some of the challenges and implications related to geographical constraints:
Increased travel time and fuel consumption
The physical limitation (geographical constraints) can lead to longer travel distances and more fuel consumption due to suboptimal routes or detours. This adds to the expenses and also hampers the operational efficiency.Necessity for real-time monitoring and adjustment
Geographical constraints are dynamic and change with time. Therefore to ensure efficient route planning, it becomes crucial to consider real-time monitoring and adjustments.Impact on delivery schedules and customer satisfaction
The delivery schedules can be disrupted due to physical limitations, leading to potential delays or customer dissatisfaction. This is the reason it becomes more challenging to meet the service level agreements and maintain a business reputation.Difficulty in meeting deadlines and time-sensitive requirements
It becomes difficult to comply with time-sensitive requirements and meet deadlines at the same time. For example, time-sensitive deliveries like perishable goods or urgent deliveries can cause financial implications or disruptions due to geographical constraints.
Hence, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, meet customer expectations, and improve service levels by proactively dealing with the above challenges.
Importance of Addressing Geographical Constraints
For the businesses involved in transportation and logistics, addressing geographical constraints is highly important. Effectively managing these constraints can be beneficial for the business in multiple ways:
Improve operational efficiency and reduce costs
Businesses can optimize route planning, reduce detours and minimize travel times by considering geographical constraints. This will help them to streamline logistics, improve operational efficiency, and save money on fuel consumption.Enhance customer satisfaction and delivery performance
By addressing geographical constraints, businesses can provide accurate delivery updates, avoid delays, and ensure deliveries are on time. Overall, this will help to enhance delivery performance, improve customer satisfaction, and boost the reputation of the business.Optimize resource utilization and minimize environmental impact
Businesses can optimize resources like fuel, vehicle capacity, and workforce allocation by addressing geographical restrictions. This will contribute to achieving sustainability goals by reducing carbon emissions and minimizing environmental impact.Enable better decision-making and route planning
Utilizing accurate geographical data and leveraging advanced technologies can help to deal with geographical constraints. This data helps businesses to identify the optimal routes and adapt to changing conditions proactively. As a result, it improves operational effectiveness.
This is how businesses can gain a competitive edge and improve customer satisfaction by identifying the importance of addressing geographical constraints.
Conclusion
Overall, geographical constraints play a pivotal role in route planning and execution of efficient transportation. And these constraints come with challenges like increased travel time and impact on delivery schedules.
Hence, resolving the geographical constraints is essential as it improves operational efficiency and enables better decision-making. Further, to deal with the challenges and implications posed by geographical constraints, businesses need to invest in advanced technologies such as route optimization software to streamline their operations.
Author Bio
Rakesh Patel
Rakesh Patel, author of two defining books on reverse geotagging, is a trusted authority in routing and logistics. His innovative solutions at Upper Route Planner have simplified logistics for businesses across the board. A thought leader in the field, Rakesh's insights are shaping the future of modern-day logistics, making him your go-to expert for all things route optimization. Read more.
Last Update: December 3, 2024